As first reported by OpenGov Asia, healthcare systems worldwide are struggling to keep pace with the demands of ageing populations and rising chronic illness. In response, researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) are advancing a new wave of medical technologies that combine robotics and artificial intelligence (AI). Their latest breakthroughs span surgical precision, rehabilitation assessment, and home-based respiratory monitoring — all designed to improve patient care while supporting clinicians.

Source: innovationhub.hk.
Ultra-small surgical robot expands access and precision
One of HKUST’s standout innovations is an ultra-miniaturised surgical robot with a diameter of just 0.95 millimetres—small enough to navigate tight, delicate spaces in the human body like bronchial or fallopian tubes. Despite its size, the robot is a fully capable surgical assistant, integrating imaging, navigation, drug delivery, and thermal therapy capabilities. Its compact form factor not only reduces invasiveness but opens new possibilities for minimally invasive procedures in previously unreachable anatomical areas.
AI-driven tools for rehabilitation and respiratory care
HKUST’s second innovation, PhyTac, is a cone-shaped handgrip embedded with 368 sensors that mirrors the spiral pattern of Aloe polyphylla. Designed to track motor recovery in patients, especially those undergoing stroke or neurological rehabilitation, the device uses AI to detect subtle changes in grip strength and force distribution, allowing clinicians to assess recovery in real time with greater accuracy than traditional methods.
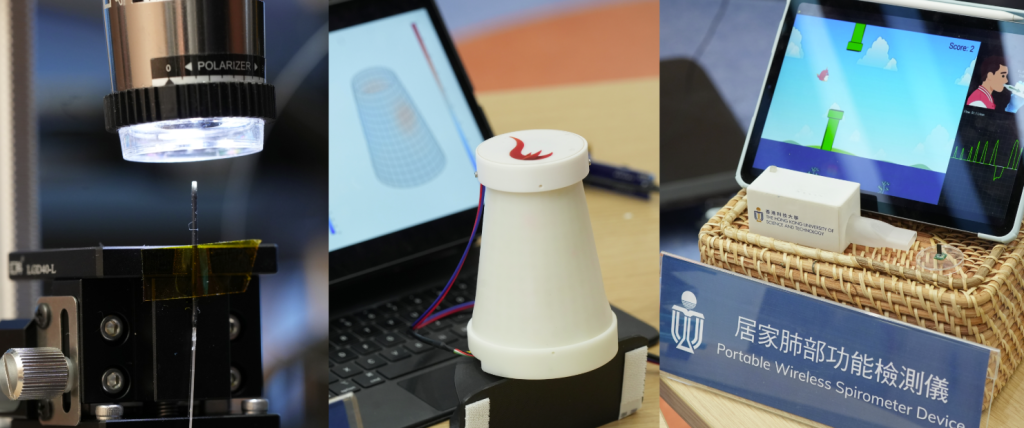

Source: hkust.edu.hk.
The third device addresses a post-pandemic focus on respiratory health: a portable, 78-gram wireless spirometer that combines clinical utility with user engagement. The system’s gamified interface—in which users control a virtual bird by breathing—encourages regular use while collecting data for remote monitoring by healthcare providers. This not only enhances compliance but also makes routine testing more engaging and accessible.
Human-centric design meets future-forward healthcare
These devices underscore HKUST’s commitment to developing intelligent tools that merge technical excellence with practical usability. By focusing on miniaturisation, AI-powered sensing, and user-friendly interfaces, the researchers are creating medical technologies that fit seamlessly into both clinical environments and patients’ daily lives.
HKUST’s innovations represent a broader shift in healthcare towards collaboration between humans and intelligent machines. By enhancing the precision, awareness, and accessibility of medical devices, their work not only meets urgent global health needs but also sets a precedent for how robotics and AI can humanise, rather than replace, modern medicine.